The Blockchain Interoperability Dilemma: Why we need Cross-chain Communications
An Overview of Blockchain Interoperability, Cross-Chain Communications, Current solutions and Challenges
Once upon a time, there was just Bitcoin, but now we have Ethereum, Cosmos, Solana, side chains like Polygon, Level 2's like Arbritrum, and many more chains all built for specific purposes, with a ton of users and Dapps.
It is now clear that we are heading towards a multi-chain future. Recent events such as the EPNS rebrand as Push Protocol as well as the emergence of multiple blockchains and protocols supporting multiple chains are proof of that. To benefit from the strengths of the different chains and protocols, and make web3 adoption and onboarding much smoother, it is important for independent chains to be able to communicate with each other.
In this article, we will be discussing blockchain interoperability, cross-chain communications, existing solutions, and challenges in solving this problem.
What is Blockchain Interoperability?
Blockchain interoperability simply means allowing different blockchain protocols to communicate and exchange data with each other.
Interoperability between blockchains refers to a range of methods that allow blockchain layers to listen to each other and transfer data, messages, and funds between each other. Being able to make a direct payment from an application on Cosmos to an account or application on a separate chain such as Solana, would be an example of blockchain interoperability.
It is important to note that cross communications between blockchains are still yet to be fully realized although a number of projects and protocols have made a lot of progress in trying to give a solution.
Why Cross-chain Communications are Important?
The million-dollar question, is why do we need cross-chain communications anyway? The short answer is to create a better experience for web3 users and unlock the benefits and strengths of current and future blockchains.
The long answer? Let's take a look at the web3 onboarding process. Do you remember how you got started?
You probably learned about web3 and got started with a specific blockchain such as Ethereum. You set up your wallets, got some ETH, perhaps purchased an NFT, and possibly got rugged in the process.
Perhaps you eventually learn about a cool application/ project on another blockchain like Solana and want to check it out. You should be able to use your wallets and ETH to buy into this Solana project right? Wrong, you find out your ETH only works on the Ethereum blockchain.
So, you start the process all over again, get a phantom wallet, convert your ETH to Sol through an exchange and now you’re finally able to make your purchase and you repeat this over and over for each blockchain you use. With just one blockchain, it's easy to navigate, make transactions, and onboard people to web 3.
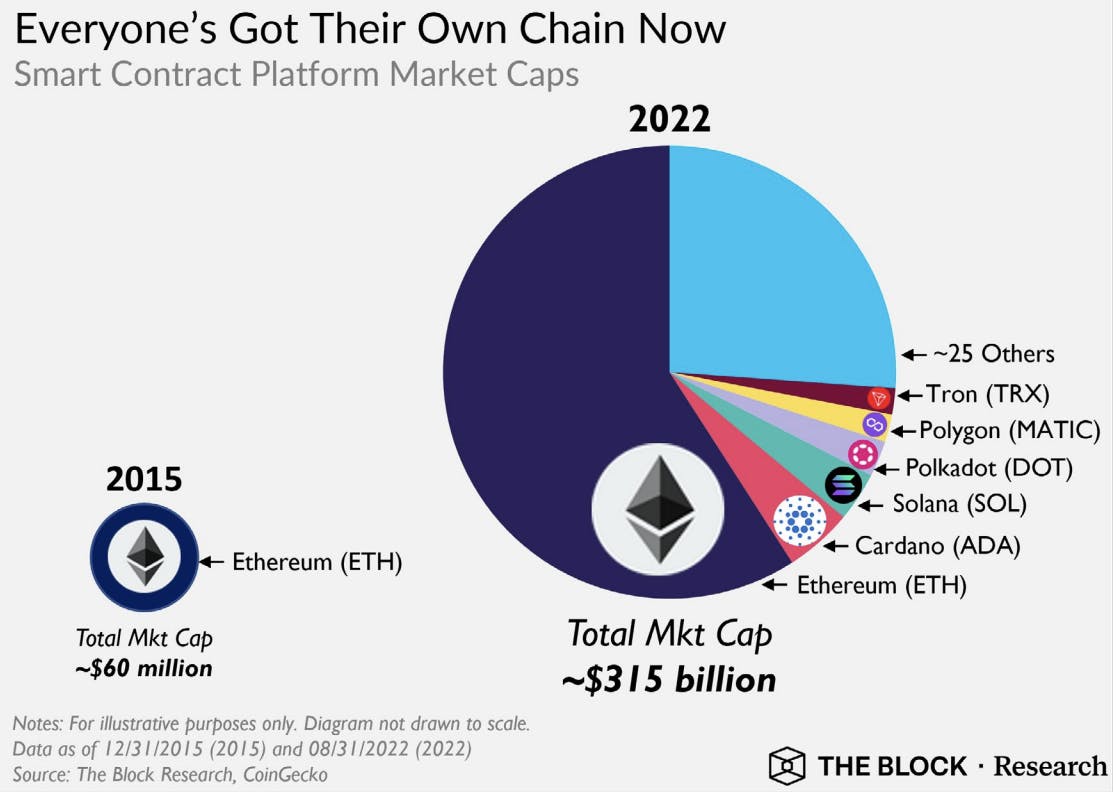 Source: the block research
Source: the block research
Unfortunately, with the blockchain trilemma, blockchains, and protocols, have to make various tradeoffs in their design and implementation regarding their security, scalability, level of decentralization, or other features. As a result, many more layer 1, layer 2 and modular blockchain solutions are being built for specific purposes, however, these blockchains, exist in silos and are largely incompatible with each other.
What if you were able to send things across to users from other blockchains without being a user of that chain yourself? Similar to how you can send an email to someone who uses Gmail as their email provider from your Proton email ID. An example of this would be sending an airdrop of ETH to users on Solana or being able to make payments in ETH on any Dapp regardless of what chain it is on.
As the web3 industry continues to grow and advance, we can expect to see even more independent blockchains as well as chains with multi-chain frameworks. Communications between them will benefit the entire ecosystem and remove current barriers in onboarding new users, building Dapps, and enjoying the value of blockchains working with each other.
Advantages of interoperability between blockchains
Improved Scalability because applications are able to leverage the speed of blockchains optimized for faster transactions and scalability.
Transfer of Data and assets between blockchain networks, which is one of the biggest advantages.
Lower Barrier of entry as you are able to build on a specific blockchain that suits your needs and still allows your app to interact with other chains or onboard users on other chains. You are also able to build more chains and protocols for specific purposes knowing you can still benefit from other chains if you would like to. This also helps with decentralization as it allows other players to come in and discourages the monopoly of blockchain users on a single protocol or chain.
Some Interoperability solutions
According to their use case, we can broadly divide the Interoperability networks and protocols into 4 main categories: Layer 1 bridges, Layer 2 Bridges, Cross-Chain Liquidity protocols, and Universal Interoperability Networks. We will be taking a look at these four categories as well as a few other interesting protocols.
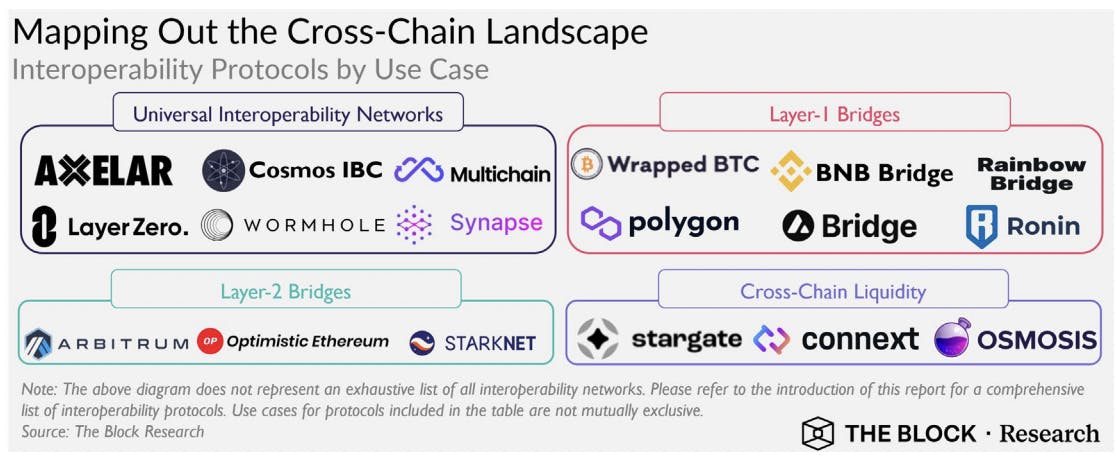 Source: The block research
Source: The block research
Layer 1 Bridges
We have layer 1 bridges that allow token transfer between two layer 1 chains, they however don't transfer arbitrary data and are typically built and operated by the organization that developed their respective layer 1 chains. Examples include BNB Bridge, Polygon Bridge, Ronin, and Rainbow bridge
Layer 2 Bridges
Layer 2 bridges, allow the transfer of value between layer 1 and layer 2 chains. They are typically built and operated by the layer 2 protocols just like with layer 1 chains, they however do not allow the transfer of data and assets between two layer 2 chains. Examples of these include Arbitrum, Optimism, and Starknet.
Cross-Chain Liquidity Protocols
Decentralized exchanges (DEX) or Cross chain liquidity protocols are a solution that allows users to swap assets on one blockchain, with other assets on the same chain. Some DEXs allow cross-chain swaps but they largely depend on third-party liquidity providers in order to do this. Some examples of DEXs include Osmosis Zone (the largest cross-chain DEX), Stargate, and Connect.
Universal Interoperability Networks
Universal Interoperability networks, allow the exchange of arbitrary data across independent layer 1 and 2 networks. They support a lot of use cases such as fungible and non-fungible token transfers, cross-chain smart contract calls, and more due to their ability to allow arbitrary data transfers. I love this category of solutions because they allow more than just token transfers and in their current implementations, they support data transfer between 10 - 50 chains with plans to support additional chains. Examples of these include Axelar, Cosmos IBC, MultiChain, Layer Zero, Wormhole, and more.
Oracles (Chainlink CCIP)
Oracles allow the transfer of information between off-chain and on-chain environments and Chainlink is a decentralized oracle service that does this. Chainlink cross-chain interoperability protocol (CCIP) in particular, has a universal messaging interface that allows smart contracts to communicate across blockchain networks and will give the opportunity to build Defi apps that allow multi-chain communications. Chainlink CCIP is not yet released and you can read more about what to expect from it here.
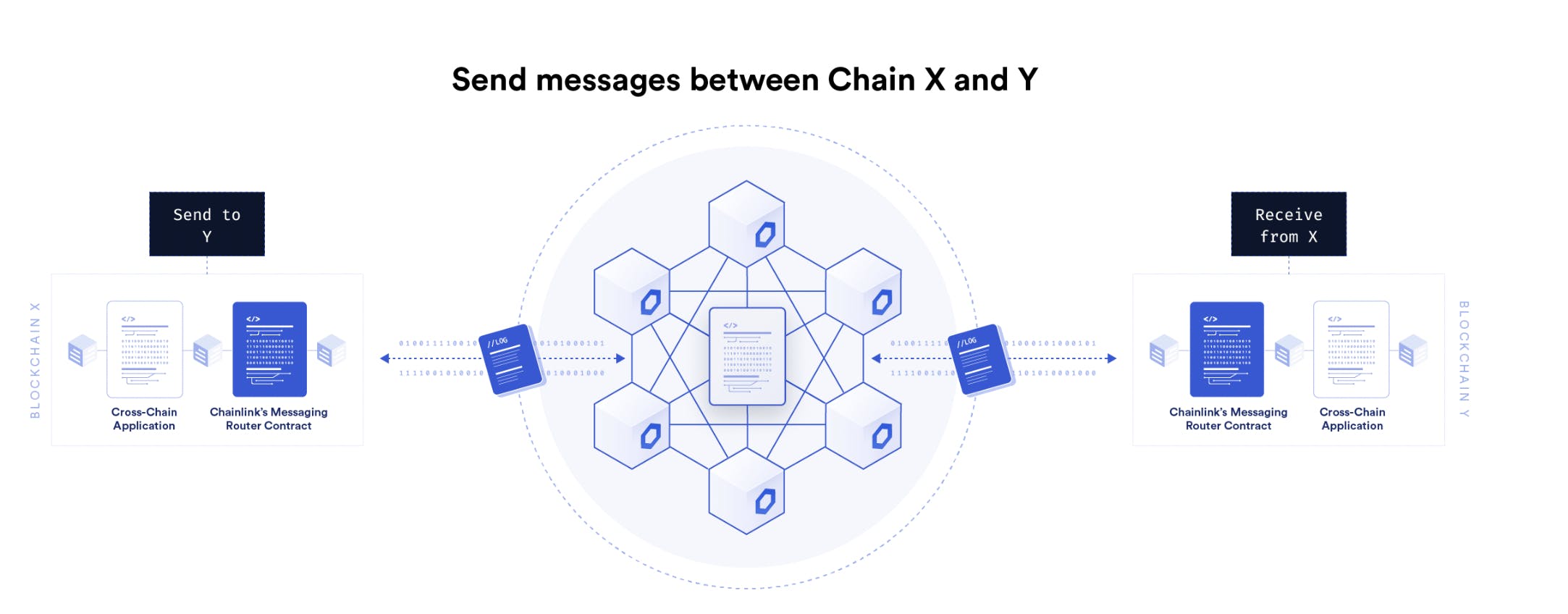 Source: Chainlink
Source: Chainlink
Cosmos IBC
The Cosmos Inter-blockchain communication protocol (IBC), is essentially an interoperability protocol that powers the cross-chain communications in the Cosmos ecosystem. This protocol connects Cosmos chains and allows the passage of arbitrary data between them. It consists of a transport layer that provides the infrastructure for data packets to be sent, authenticated, and interpreted by the respective chains and layers. There is also the application layer on which cross-chain applications can be built.
Osmosis Zone and Axelar
One Interoperability solution I find very interesting is the partnership between Osmosis Zone and Axelar Network. Osmosis which is the Cosmos DEX with the largest liquidity pool leverages Axelars bridge service to allow the transfer or swapping of assets across chains within or outside of the Cosmos/IBC ecosystem which is huge. It also allows easy integration into Dapps as developers can just use the available APIs and essentially plug and play without having to learn a new code base for each chain etc. A sample use case is
Challenges
We have seen a significant increase in the adoption and usage of interoperability solutions, however, there are still challenges such as :
Security Concerns
Even with rigorous security audits, we see bridges and other interoperability networks get hacked. This in turn results in lesser trust in these solutions due to the potential risks involved. Different chains have different consensus mechanisms, security layers, and frameworks and the transfer of assets between them introduces weak points that can and have been exploited in the past. For mainstream adoption of interoperability networks, we will need to have better security.
 Another bridge got hacked again...
Another bridge got hacked again...
Developer Adoption
Different chains have different development environments and languages which adds complexity for developers in integrating cross-chain transfers in their decentralized applications. Interoperability protocols like Osmosis, Cosmos, and Axelar are abstracting away some of that complexity on the backend and making integrating cross-chain communications easy for developers however, this whole concept is still new to a lot of blockchain developers and so there is a need for more education, onboarding and better products/ networks with great UI/UX for the developers.
Conclusion
Cross-chain communications, is very crucial for the multi-chain future to be fully realized. However, interoperability between blockchains, is a very hard problem to solve. Current cross-chain technologies, will need to be developed further and security on a lot of these networks will need to be addressed. Axelar, Cosmos, Osmosis and Celestia are protocols to keep an eye on and the launch of Chainlink CCIP is highly anticipated. Will there be new players that will change the game completely? Going by the rate of development in this space, I can almost guarantee that there will be and I am looking forward to see how it all plays out
TLDR;
We are heading toward a multi-chain future, and for that to be a reality, we need interoperability between blockchains i.e blockchains being able to send data to each other. This would improve the onboarding process and general user experience of decentralized applications. Certain solutions like bridges, oracles, cross-chain liquidity protocols, and protocols that allow the transfer of arbitrary data between blockchains are currently in development. There are however still security concerns and low adoption of these protocols.
Also, just read the article :)
Source Links
- Article - Understanding Cross-Chain Communication – Examining Blockchain Interoperability and Why It Matters
- Article - Blockchain Interoperability – How Does It Work?
- Article - Blockchain Interoperability – Understanding Cross-Chain Technology
- The Block Research - Interoperability Networks: Infrastructure for the Multi-Chain Future
- Article - Cross-Chain Interoperability: What it Means for Blockchain
- Article - Osmosis Is Building a Cross-Chain Liquidity Layer With Axelar
- Website - Cross-Chain Interoperability Protocol (CCIP)
- Website - Cosmos Inter-Blockchain Communication Protocol
